Why do online stores need SEO? Search Engine Optimization helps to increase
a website ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) of such search engines like Google & Bing. Developing an SEO audit & strategy for your e-store can bring motivated traffic to your website, as well as grow your sales and revenue.
a website ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs) of such search engines like Google & Bing. Developing an SEO audit & strategy for your e-store can bring motivated traffic to your website, as well as grow your sales and revenue.
Magento SEO Audit. What do we offer?
We interviewed our customers to learn the main challenges they faced in launching the SEO strategy and how Amasty can help with it. Many customers said that the main problems are
a qualified technical SEO audit and setup.
We are ready to analyze your online store and uncover all critical technical issues and incorrect redirects. Then during the audit our Magento SEO expert will immediately solve fast-to-fix on-site problems and give you an ultimate guide on how to fix the rest
by yourself. We will also provide estimates for the required time to fix all of the SEO issues on your website by Amasty team
& advise you on how to choose a good SEO specialist
for the future.
a qualified technical SEO audit and setup.
We are ready to analyze your online store and uncover all critical technical issues and incorrect redirects. Then during the audit our Magento SEO expert will immediately solve fast-to-fix on-site problems and give you an ultimate guide on how to fix the rest
by yourself. We will also provide estimates for the required time to fix all of the SEO issues on your website by Amasty team
& advise you on how to choose a good SEO specialist
for the future.
Technical SEO Audit

SEO Toolkit with qualified setup replaces 80% of a full-time SEO-specialist. But are you sure that you can set up SEO-toolkit extensions with maximum value?
We will configure this module specially for your online store
so that SEO Toolkit works at 100% of its efficiency. Our SEO specialists will also give you a checklist for setting up this module and you will be able to further set it up for an online store yourself.
We will configure this module specially for your online store
so that SEO Toolkit works at 100% of its efficiency. Our SEO specialists will also give you a checklist for setting up this module and you will be able to further set it up for an online store yourself.
Set up SEO Toolkit

Who is the Technical SEO Audit for?
Dreaming about high Google rankings at limited resources?
We will be happy to offer
a ready-made solution that covers all the SEO needs
of your e-store.
We will be happy to offer
a ready-made solution that covers all the SEO needs
of your e-store.
Store Owners

We will be happy to help if you do not have enough skills/time at your Magento SEO agency
Also, we have a lot of experience in SEO and we know the nuances of setting it up for Magento.
Also, we have a lot of experience in SEO and we know the nuances of setting it up for Magento.
Agencies

Why can you trust us?
of users on amasty.com come from organic search. Why is organic traffic important? Organic traffic is important because it brings high-motivated users and generates most conversions at an e-store.
61.2%
Our Impressions (the number of times that amasty.com has been listed on a SERP (Search Engine Results Page) grew over the last year from 2.44M to 3.44M.
1M
↑
of our promotion keywords are in top-10 Google Search Results.
95%
Some typical SEO issues that you may have on your website:
HTTP 301 or Moved Permanently
This response status is usually used for permanent redirects, for example, when your website has moved to another URL. To check if you have this issue, open the page and hover your mouse over the link in your content. In the bottom-left corner, you will see its URL:
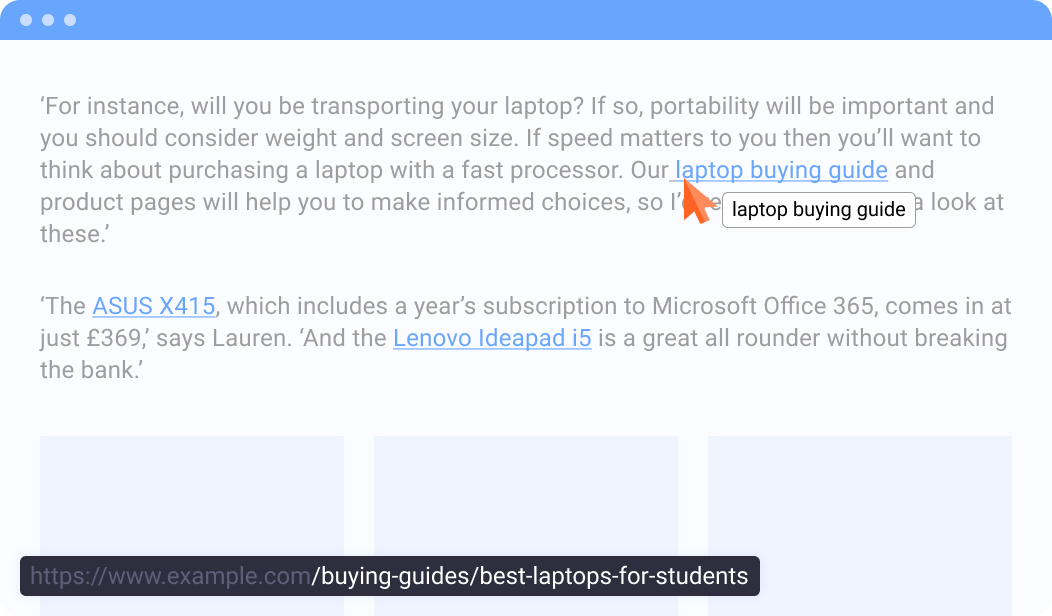
If, after clicking on the link, you are redirected to another page with a different URL

then this is a typical mistake that can lead to a decrease in positions on Google search result pages.
Error 404 or Not found
This error typically means that the link you wanted to access couldn't be found on the website server. So, if you click on the link in the menu or text and get a blank page or a 404 error, this may decrease your position on Google search result pages.
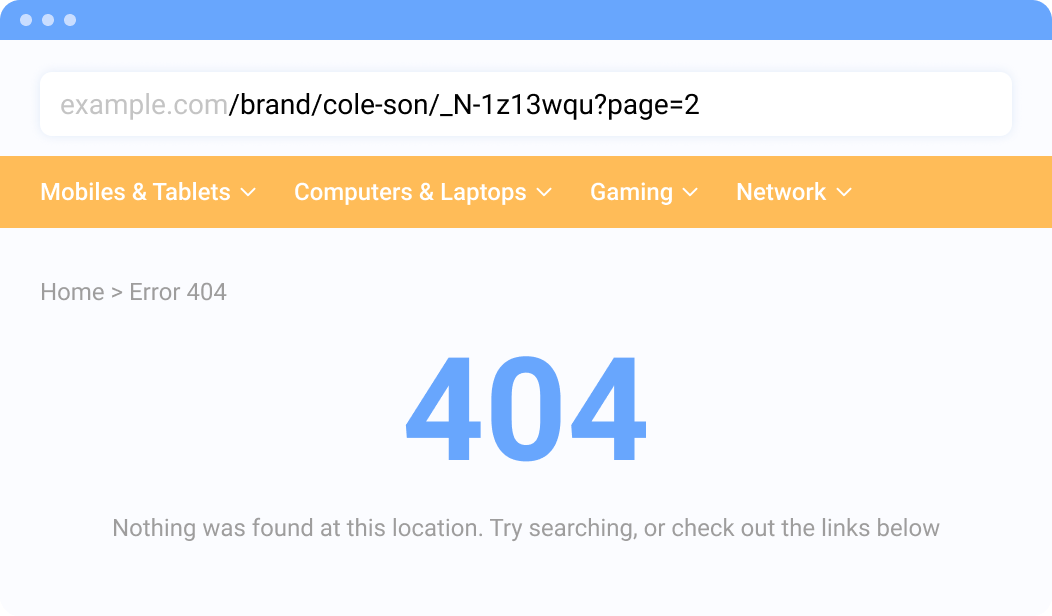
This happens because user behavior is one of the most important ranking factors, and seeing error 404 is one of the most frustrating things for your visitors. As a result, users leave your website immediately, increasing your website bounce rate.
A too long title
To check if you have this issue, right-click on your page in the browser and choose View Page Source at the bottom of the list. In the new-opened window, you can check your <title> meta tag. It shouldn't be longer than 70 characters.

Otherwise, your title will be cut on a search result page in Google, and the "extra" words will be replaced with an ellipsis. Sometimes Google can replace your long title with a more appropriate one.
Title equals H1
If you don't fill in the meta title for the page, it will be automatically replaced with your H1. To check if you have such an error, right-click on your page in the browser and choose View Page Source at the bottom of the list. In the new-opened window, you can see meta tags <title> and <h1>.
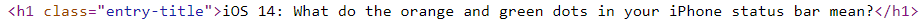
Otherwise, your title will be cut on a search result page in Google, and the "extra" words will be replaced with an ellipsis. Sometimes Google can replace your long title with a more appropriate one.
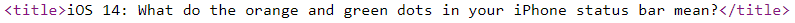
Canonical URLs
Say you have a catalog with multiple pages that are numbered 1st, 2nd, etc. like this:

Tag 'canonical' is used to avoid duplicate content and mark one page as a preferred one. If you have a wrong URL under this tag, it may decrease your positions on search result pages in Google. To check what page is marked as canonical, go to the second page of your catalog, right-click on your page in the browser and choose View Page Source at the bottom of the list. In the new-opened window, find the <link rel = "canonical"> meta tag.

This link should differ from the URL of the opened page.
5
1
2
3
4
Price Options
Technical SEO Audit
from 399$*
from 399$*
Amasty's SEO Team will analyze your store and give you a unique SEO-improvement plan.
Technical SEO Audit + SEO Toolkit Configuration
from 699$*
from 699$*
Amasty's SEO Team will analyze your store and give you a personal SEO-improvement plan + optimal SEO Toolkit setup
- ★ Analyze your store
- ★ Uncover all critical technical issues & incorrect redirects
- ★ Fix fast-to-fix on-site SEO problems
- ★ Deliver an ultimate guide especially for your e-store
- ★ Provide personal consultation
- ★ Setting up SEO Toolkit in the best way
* SEO audit cost fully depends on your current site and its configuration
| GET A QUOTE |
Get a technical audit and unique SEO improvement plan
Fill in the form below and our specialist will contact you within 24 working hours
Irina Kogoleva
Business Development
Manager at Amasty
Manager at Amasty
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER!
Be the 1st to learn about our specials and new products
Be the 1st to learn about our specials and new products
Company Info
Headquarters
Corporate
About Us

Bratislava, Slovakia
Development office

Minsk, Belarus
Representative office

London, United Kingdom
Loyalty Programs
Legal








